pipeline-resources
How to read the Methylcheck report
Zymo Bioinformatics May 01, 2023
- Overview of the pipeline
- Report overview
- General Statistics
- FastQC (raw)
- Cutadapt
- FastQC (trimmed)
- Sequence Counts
- Sequence Quality Histograms
- Per Sequence Quality Scores
- Per Base Sequence Content
- Per Sequence GC Content
- Per Base N Content
- Sequence Length Distribution
- Sequence Duplication Levels
- Overrepresented sequences
- Adapter Content
- Bismark
- Picard
- CpG Coverage
- Software
- Summary
Overview of the pipeline
The report was generated with Zymo’s Methylcheck pipeline built on nextflow platform.
The backbone of the pipeline includes:
-
Input reads trimming by TrimGalore.
-
Reads quality assessment by FastQC.
-
Reads alignment by bismark.
-
Methylation calling by MethylDackel.
-
Library insert size distribution by picard.
-
Read coverage per cytosine by bedtools.
Report overview
This bioinformatics report is generated using MultiQC, which is integrated into the nextflow pipeline. There are general instructions on how to read a MultiQC report at here, or you can watch this video. In general, the report has a navigation bar to the left, allowing to quickly navigate to any section in the report. Next to it on the right are result sections, which are interactive: hovering mouse over or clicking these tables/figures will lead to more details. On the right edge, there is a toolbox that allows to customize the appearance of the report and export figures and data.
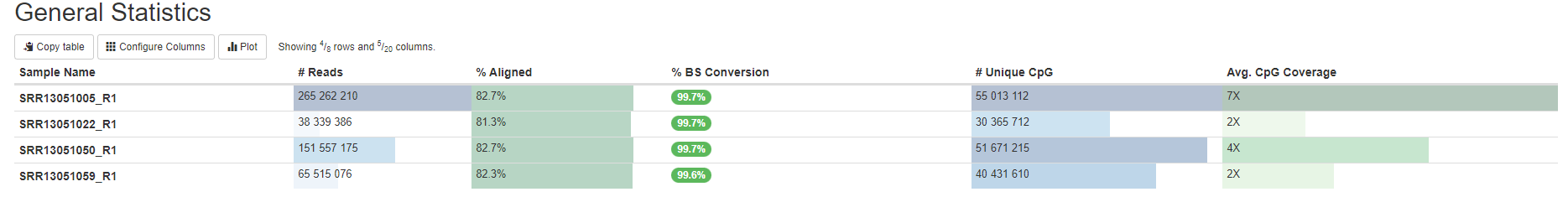
General Statistics
The table General Statistics provides some import statistics of the data. Here are some you can use to assess the data:
-
# Reads This is the total number of read pairs (or reads in single-end sequencing) contained in the FASTQ file(s) before trimming.
-
% Aligned This is the percentage of total uniquely aligned read pairs (or reads in single-end sequencing) to the target genome. In general, the higher the percentage, the better. The value however varies among sample types and library protocols. The total number of reads is shown in column
# Reads. -
% BS Conversion This metric provides another measurement on BS conversion rates, calculated as 1 minus the average methylation level in the CHG and CHH contexts, assuming no methylation at all in those two contexts. However, the assumption may not be valid in some circumstances such as in plant, so a BS conversion rate from Spike-ins is a better estimate.
-
# Unique CpG This is the number of CpG cytosines in the genome covered by reads.
-
Avg. CpG Coverage This is the average number of reads covering each cytosine as reported in the
Unique CpGcolumn. Please also refer to the section CpG Coverage for the counts of cytosines at different read coverage levels.
FastQC (raw)
This section shows the FastQC analyses run on raw fastq files. FastQC is a tool to analyze library qualities by examining the metrics such as base qualities, GC content, overrepresented and adapter sequences. A warning is issued if any metric fails.
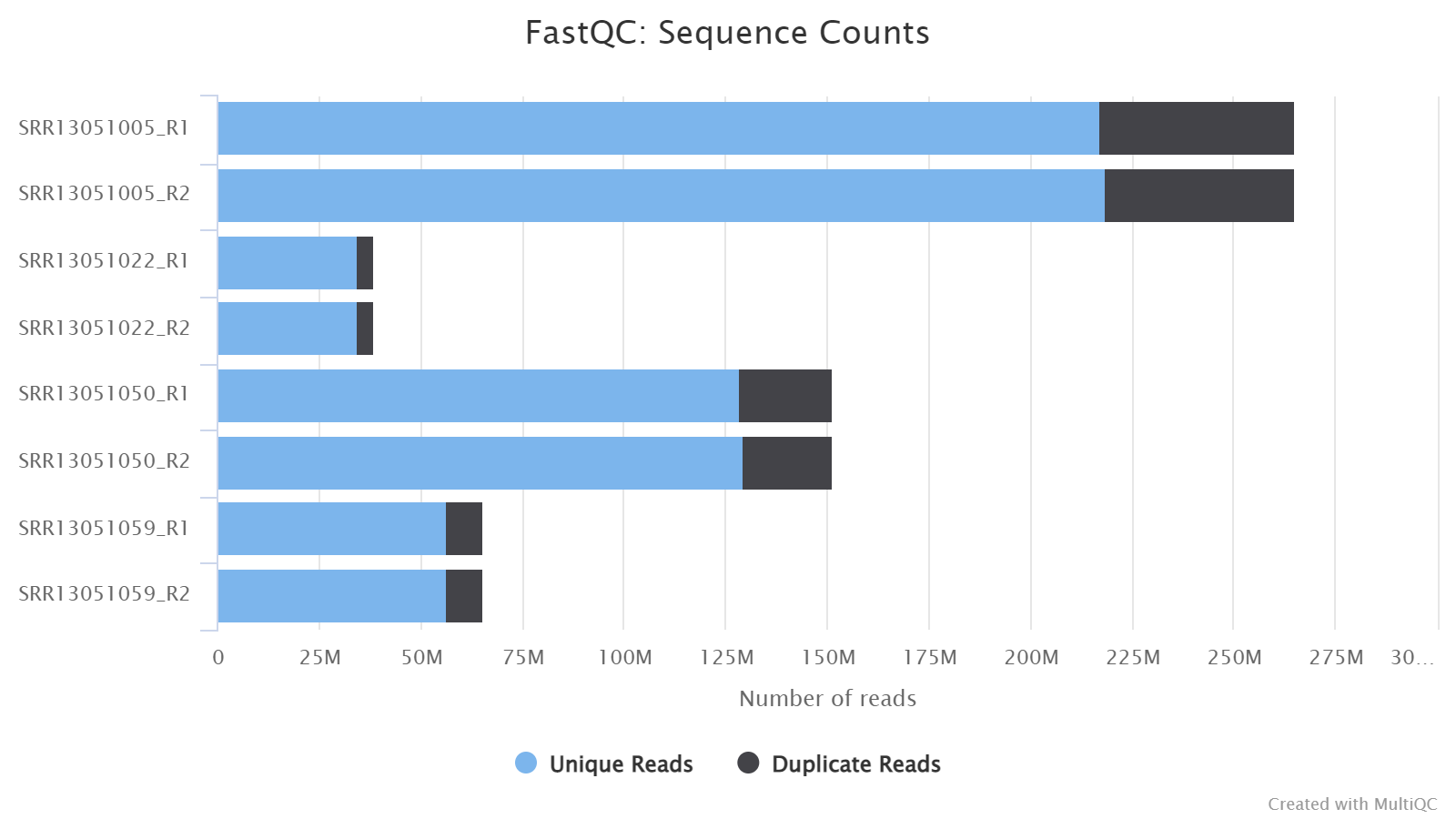
Sequence Counts
The histogram show the number of PE/SE reads for each sample. Duplicate reads are an estimate only and are separated from unique reads.
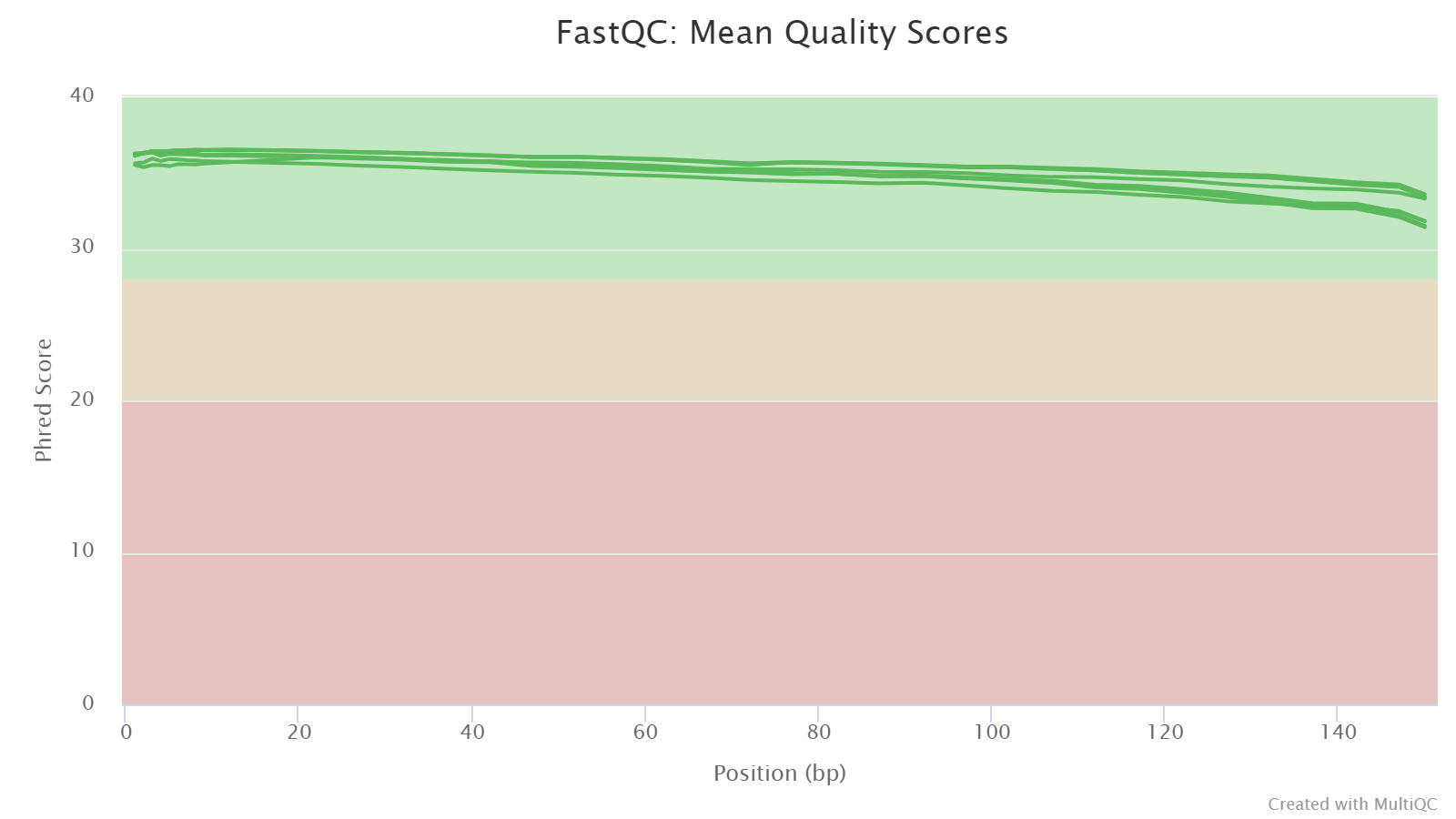
Sequence Quality Histograms
This section shows the average Phred quality scores per base along read length. Normally, the base quality decreases towards 3’end. This provides information on whether 3’end quality trimming is needed.
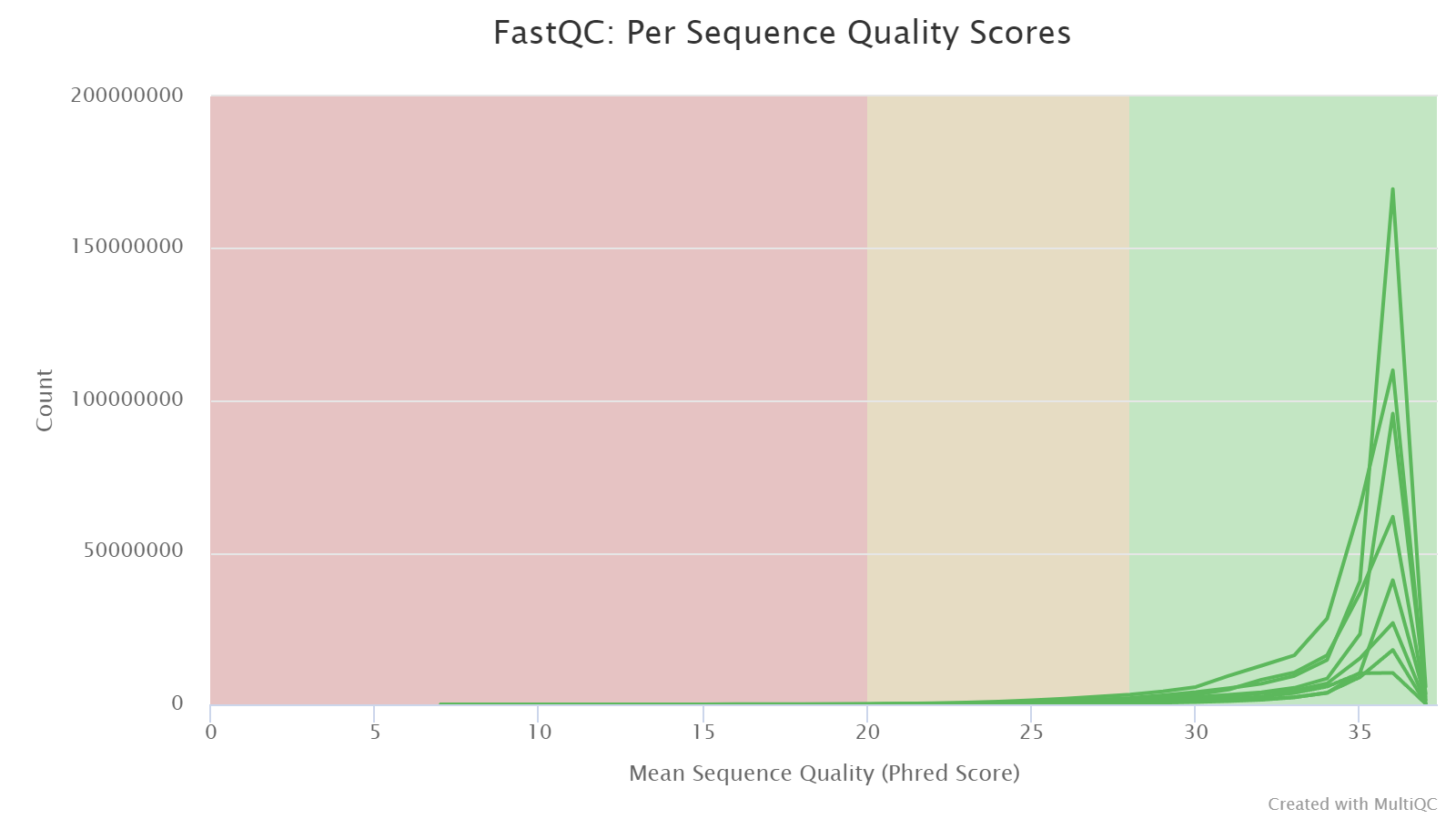
Per Sequence Quality Scores
This plot shows the distributions of read sequence quality, computed by averaging the Phred scores of all bases in a read. It is expected that peaks are at values > 28; if you see peaks at lower values, it is a warning sign of low quality libraries.
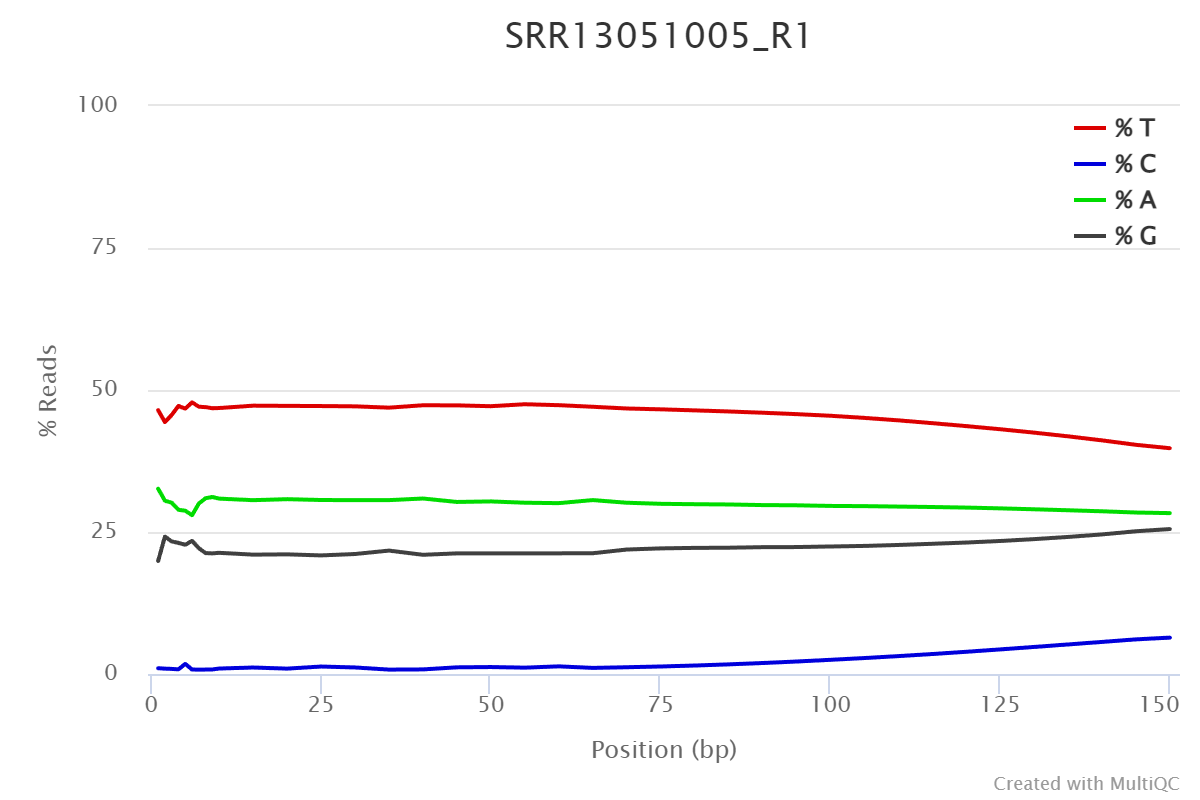
Per Base Sequence Content
This plot shows the percentages of the four nucleotides (A, T, C, G) at each read position; each base is in different color. The heatmap shows average base compositions with samples as rows and positions as columns. When hovering mouse over the plot, the nucleotide compositions are shown at top of the plot.
One can click on one row/sample to have a detailed view on how nucleotide composition changes over read length. The composition is expected to be even over read length.
Per Sequence GC Content
This plot shows the distributions of reads’ GC content, that is, the percentages of G and C nucleotides in a read.
Per Base N Content
The plots shows the percentage of an undetermined basecall N at each position. Reads with N content greater than 5% usually indicates poor sequencing quality or other technical issues.
Sequence Length Distribution
The plots provides insights into the distribution of sequence lenghs obtained
from the input fastq files. For raw reads that contain uniform sequence length, normally only a highlighted text All samples have sequences of a single length (XXX bp) should be displayed in this section. For trimmed reads, the peak of the lineplot may vary depending on the library size and some other factors.
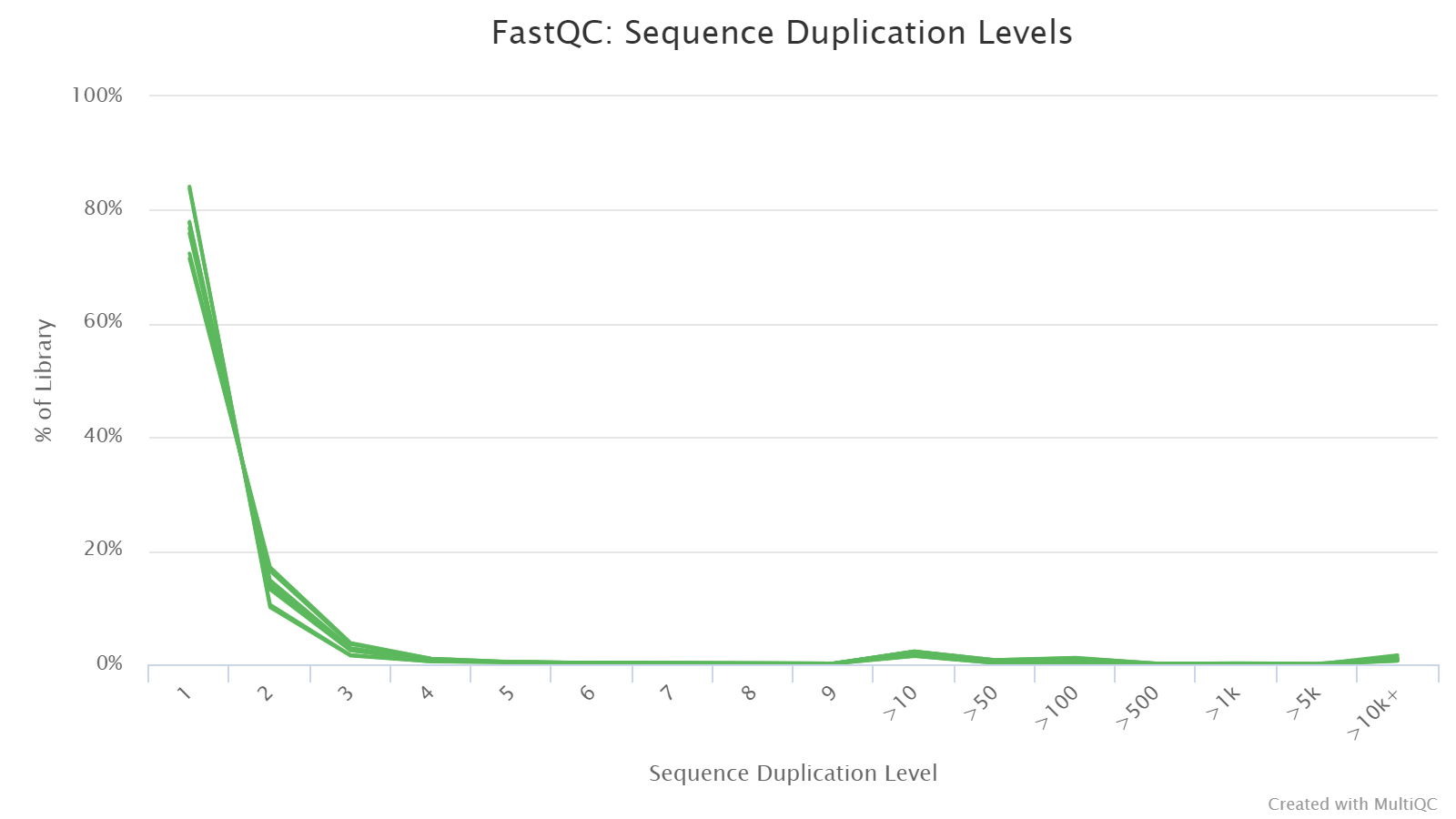
Sequence Duplication Levels
Duplicated sequences refer to the occurance of the same or highly similar reads that can arise from PCR artifacts or biological duplicats. In a diverse library like WGBS, the majority of the reads should occur only once. Therefore, the highest peak should be observed on the leftmost side of the plot. A warning will be issued if non-unique sequences make up more than 20% of the total.
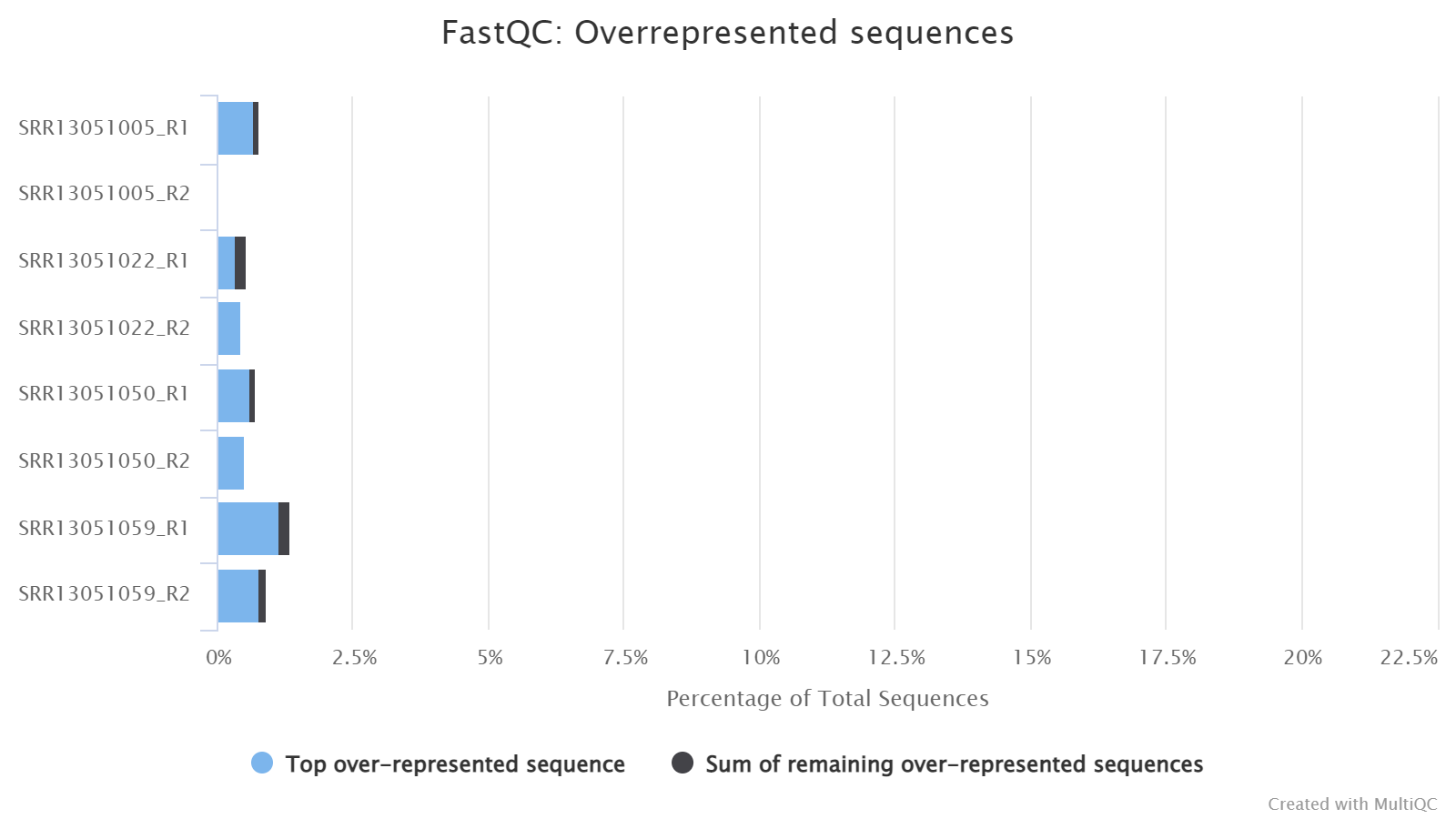
Overrepresented sequences
If there are overrepresented sequences, such as contamination, enriched fragments, or duplicated reads, this section will show the frequencies of the top representative sequences (frequency > 0.1%).
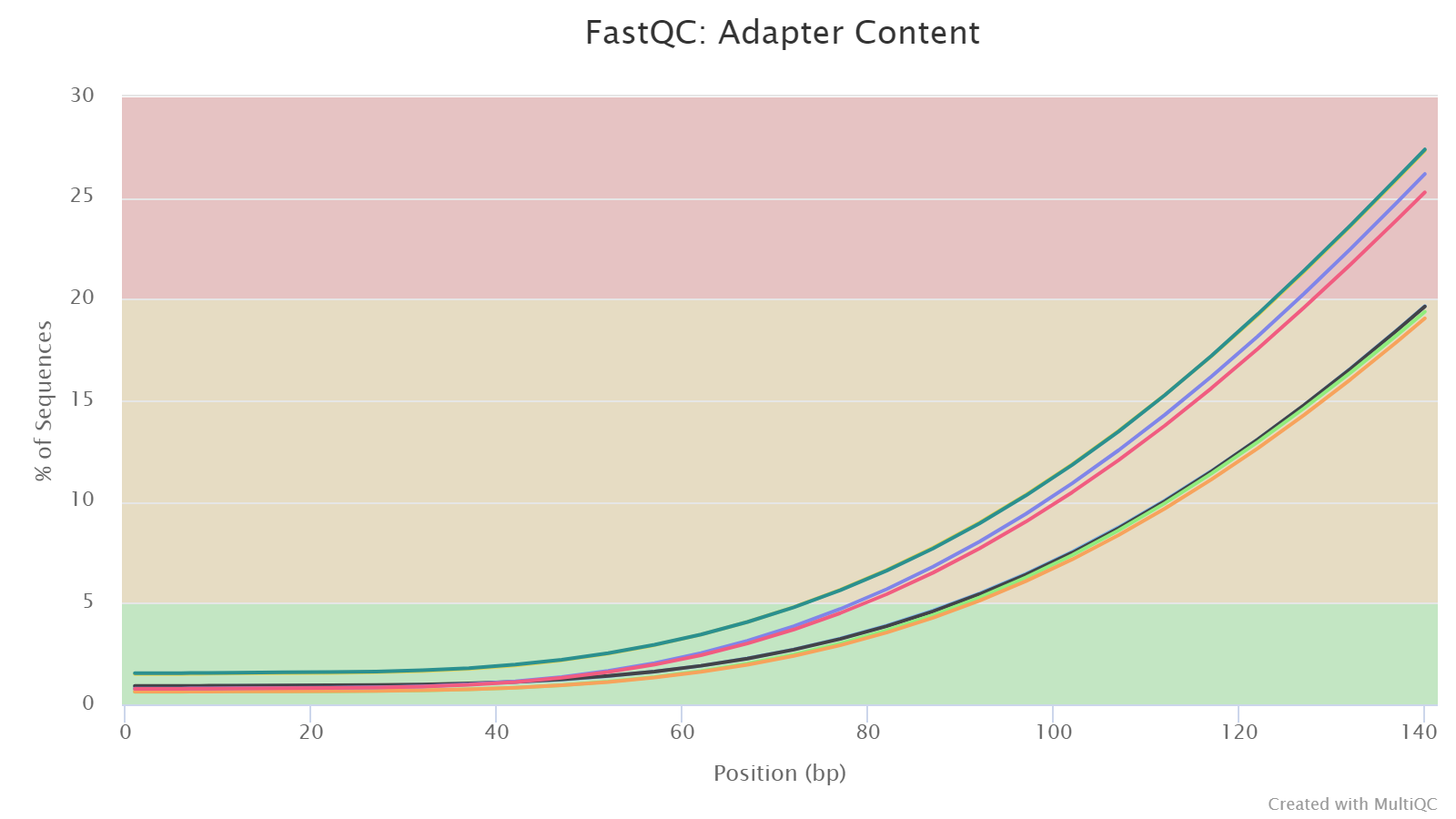
Adapter Content
This plot shows the percentage of reads containing an adapter sequence at each base position cumulatively, so if a read contains an adapter at a position, then this read is counted for all subsequent positions.
When running this analysis on already trimmed sequences, one expects to see no adapters, as displayed here.
Cutadapt
TrimGalore internally calls cutadapt to trim low-quality bases and
adapters from reads. This section presents the results of trimmed
fragments and the remained reads after trimming and filtering.
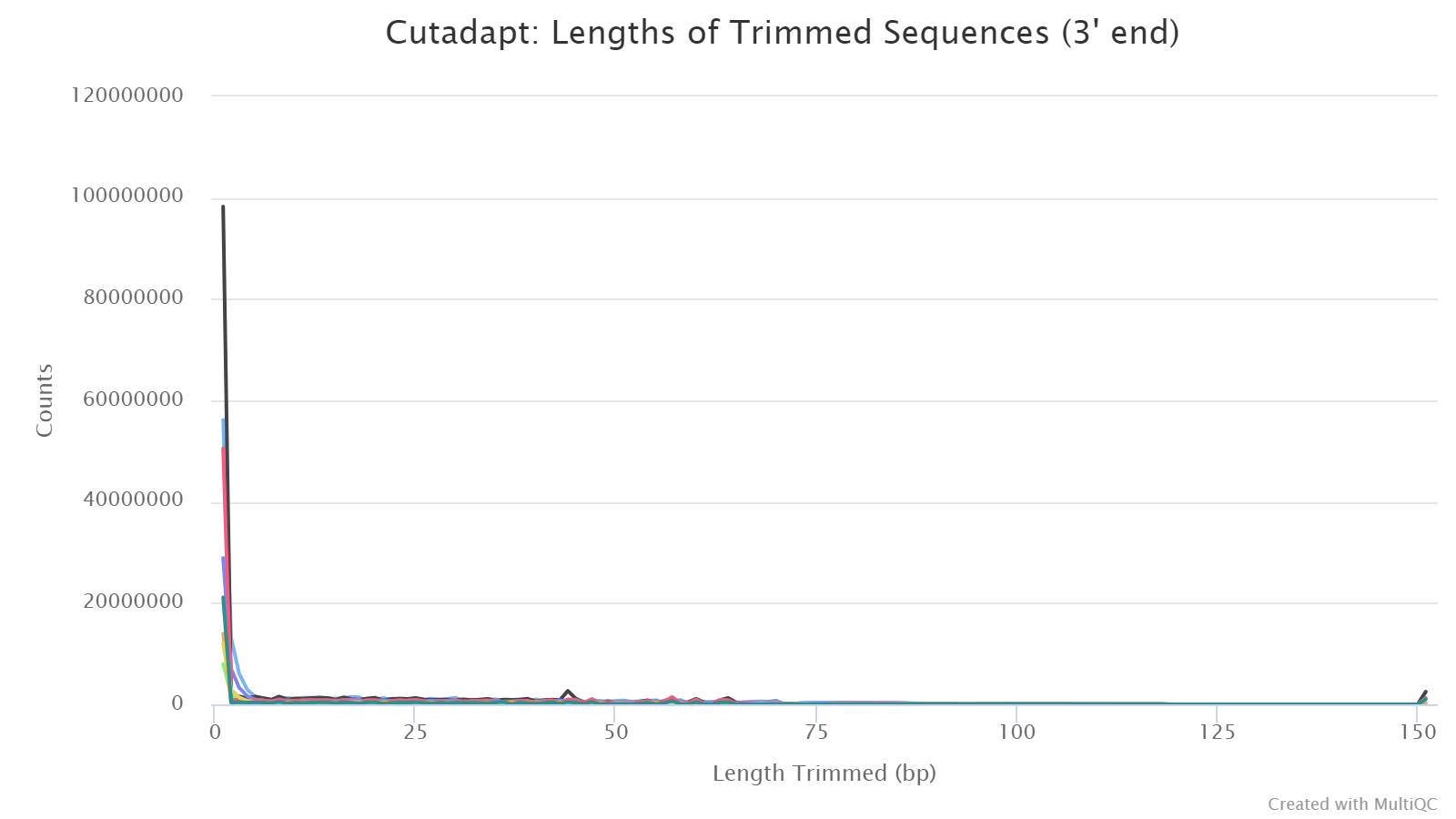
Trimmed Sequence Lengths
In this plot, the x-axis shows the length of each trimmed fragment (the part discarded), and the y-axis shows the number of reads for each case. Normally, the number drops quickly as the lengths of trimmed segments increase, because for most reads, only a few bases are derived from adapters or of low quality. For RRBS, however you may see some peaks in the middle because of short library insert sizes.
The tab Obs/Exp presents the ratio of observed and expected counts for
a given trimmed length. The expected count is computed by assuming
sequencing error only. A ratio higher than 1 indicates that some trimmed
segments are true adapters. One can see cutadapt’s
guide
for more explanation.
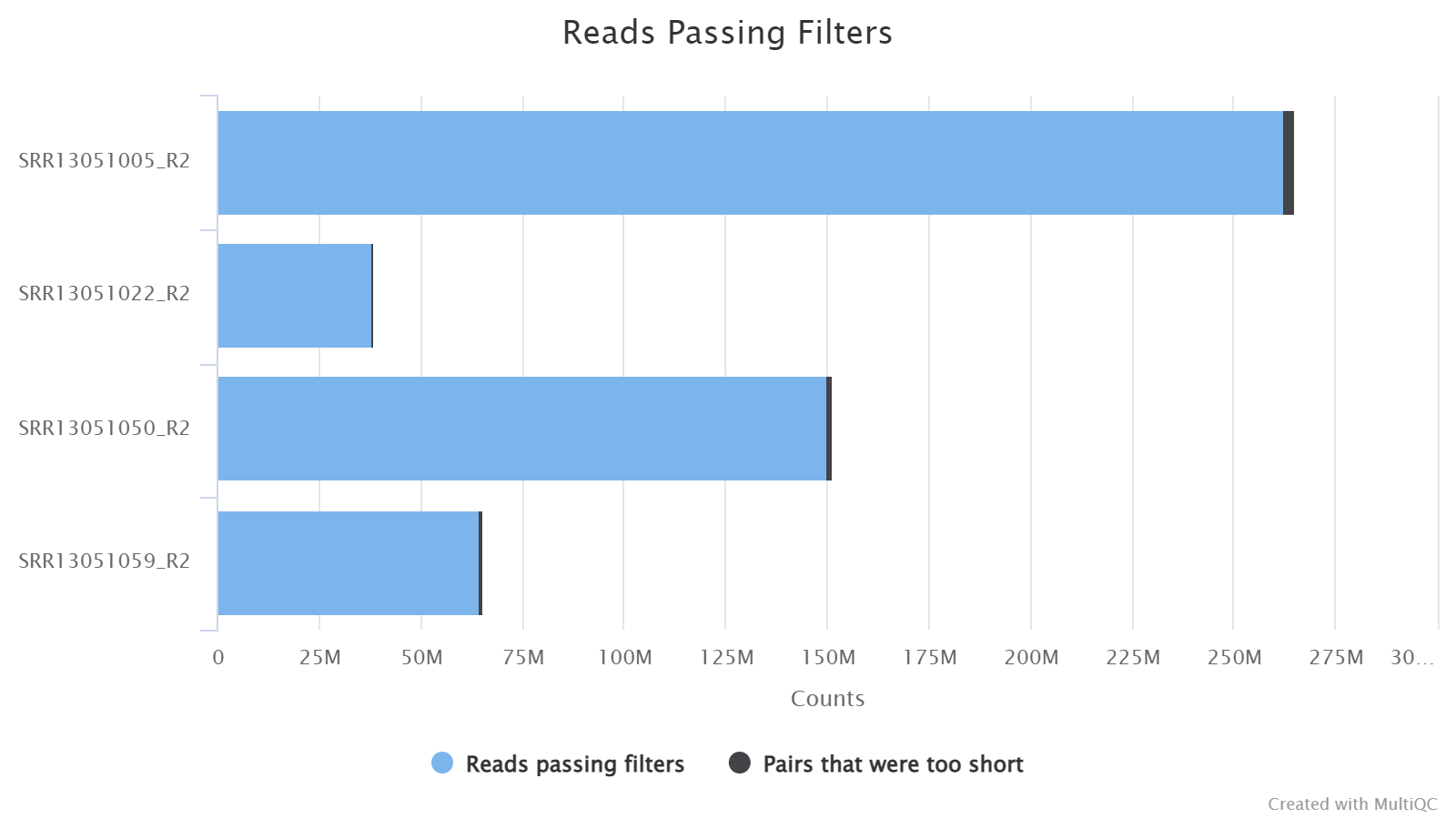
Filtered Reads
In this plot, it shows the number of reads passing the filtering of TrimGalore. TrimGalore trims low-quality bases and adapters from the 3’end of each read and filters out reads that are shorter than 20bps. And in the paired-end mode, both reads in a pair are discarded if either of them is shorter than 20 bps, and this is why the read1 and read2 files of one sample always have the same number of filtered reads.
For RRBS sequencing, the option --rrbs for TrimGalore is on to remove
filled-in bases at read ends introduced during library preparation. For
more details on how TrimGalore removes the filled-ins, please refer to
the TrimGalore
Manual.
One can toggle the tabs between Counts and Percentages to view the numbers and percentages of filtered reads, a feature available for most plots in the report.
FastQC (trimmed)
This section shows the FastQC analyses run on trimmed fastq files. By default, raw reads will go through quality trimming and adapter trimming before alignment. Please refer to FastQC (raw) because of the similar functionality.
Bismark
Bismark is a tool to align bisulfite-converted sequencing reads to a genome. One can find the manual of the program at here.
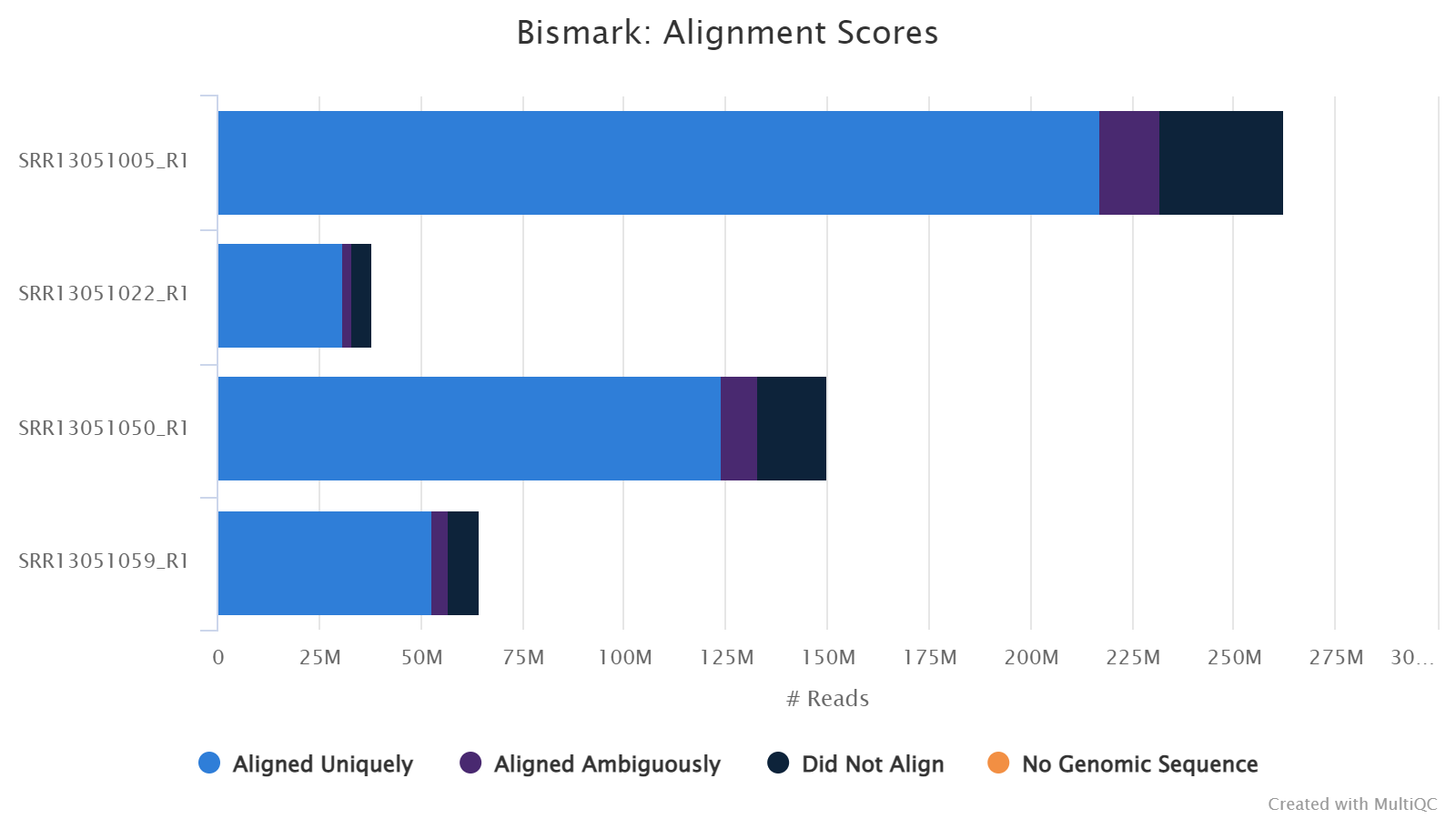
Alignment Rates
This plot shows the number and percentage of reads in each of the following categories:
-
Aligned Uniquely: reads that are mapped to a unique genomic position.
-
Aligned Ambiguously: reads that are mappable to multiple genomic positions.
-
Did Not Align: reads that are not alignable to the genome.
For downstream analyses such as calling methylation, only Aligned Uniquely reads are used.
Strand Alignment
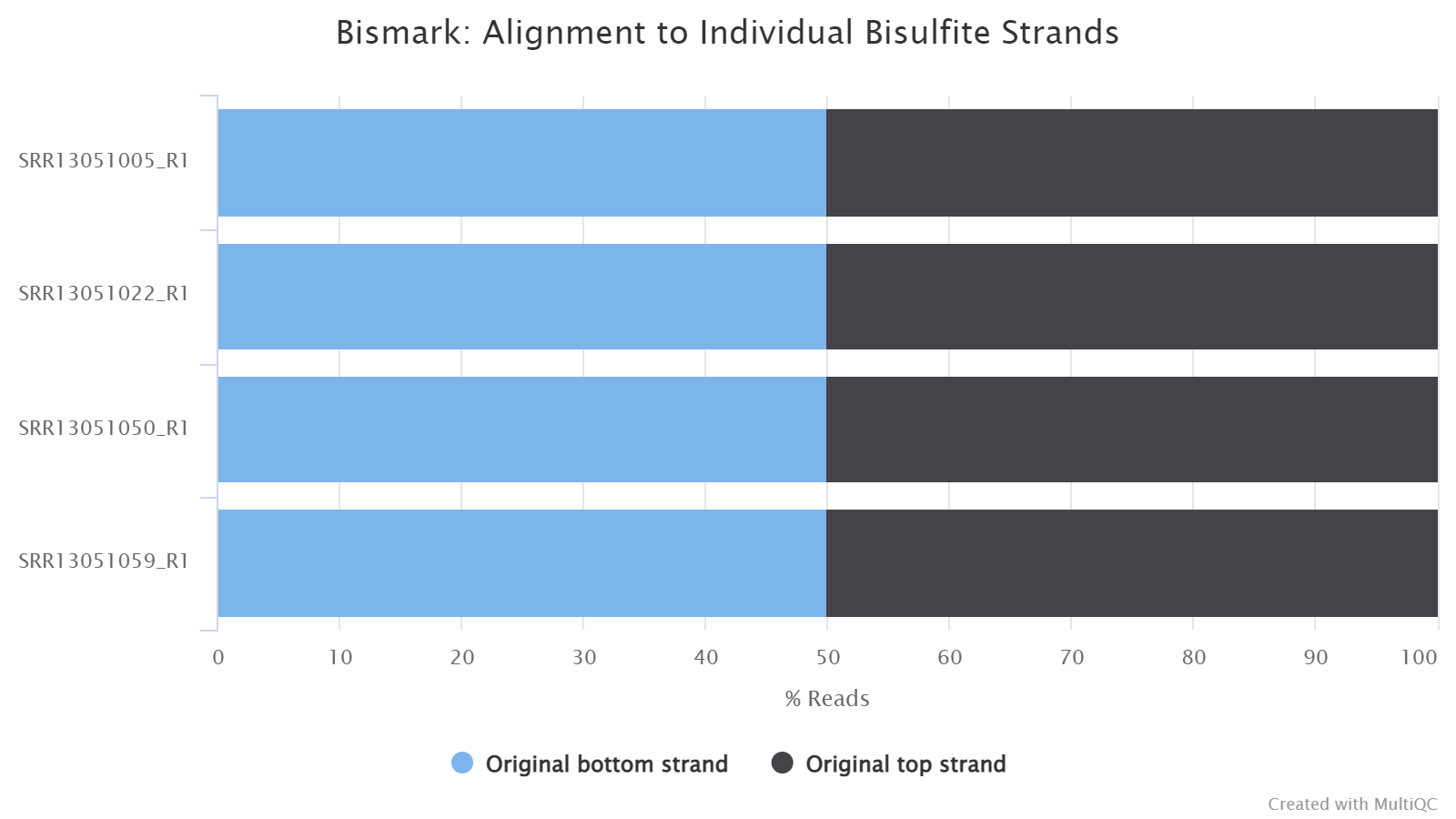
This plot shows which strand each read pair is aligned to. Due to bisulfite conversion, there are four strands that a read pair can align:
-
Original top strand: the top/Waston strand.
-
Complementary to original top strand: the strands complementary to the top/Waston strands, generated through PCR.
-
Original bottom strand: the bottom/Crick strand.
-
Complementary to original bottom strand: the strand complementary to the bottom/Crick strand, generated through PCR.
For a directional sequencing library, you may only see reads from original top and bottom strands, but for non-directional one, you will see reads from all four strands.
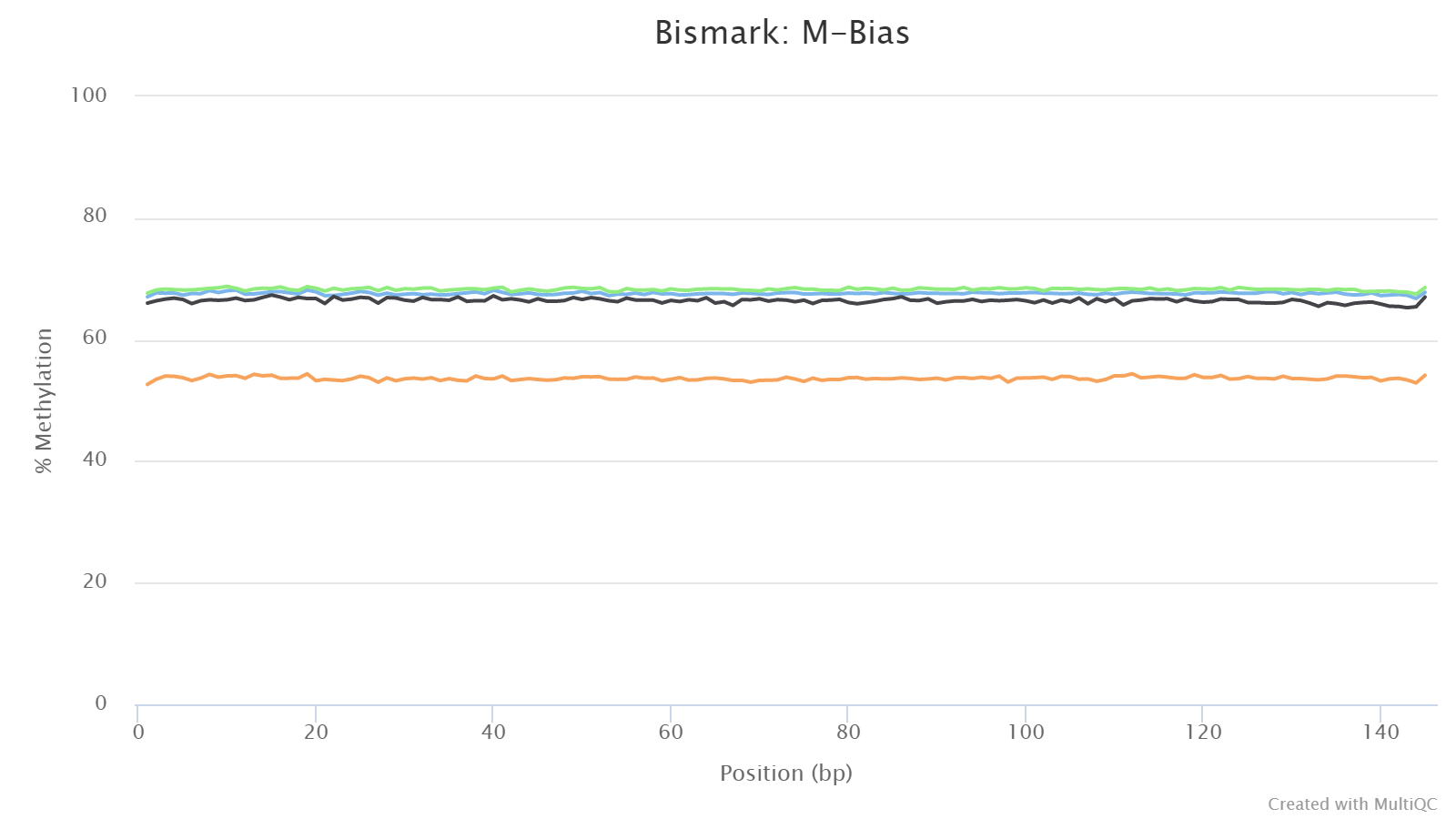
M-bias
This plot presents the methylation values along base positions in a read. The methylation value is computed by averaging the methylation values at a position across all reads in a sample. Normally, one expects the methylation value stays constant along base positions.
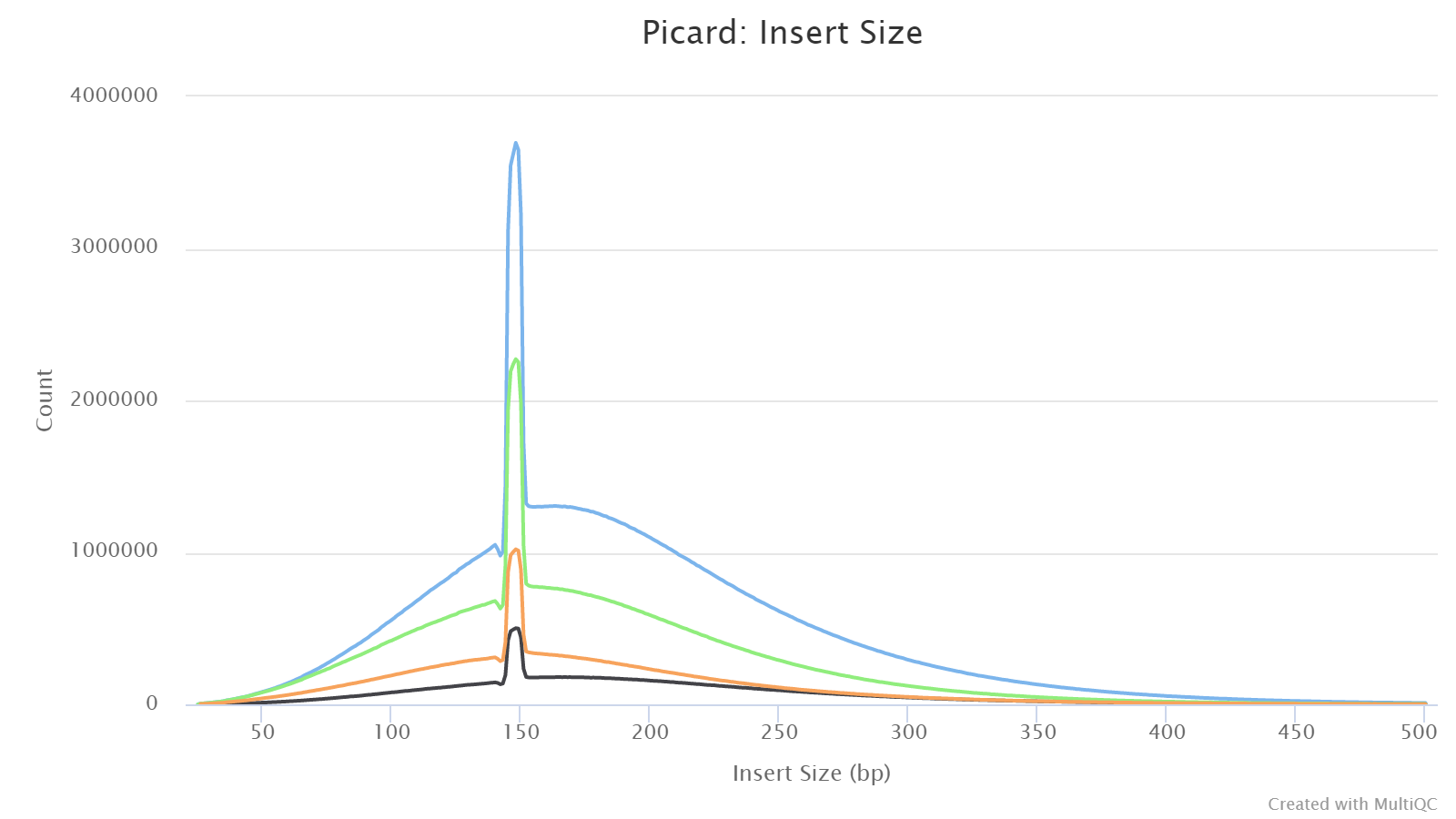
Picard
This shows the distribution of estimated insert sizes for each sample. For RRBS, one may see multiple spikes in the range from 40 to 220 bps due to MspI digestions (see explanation here).
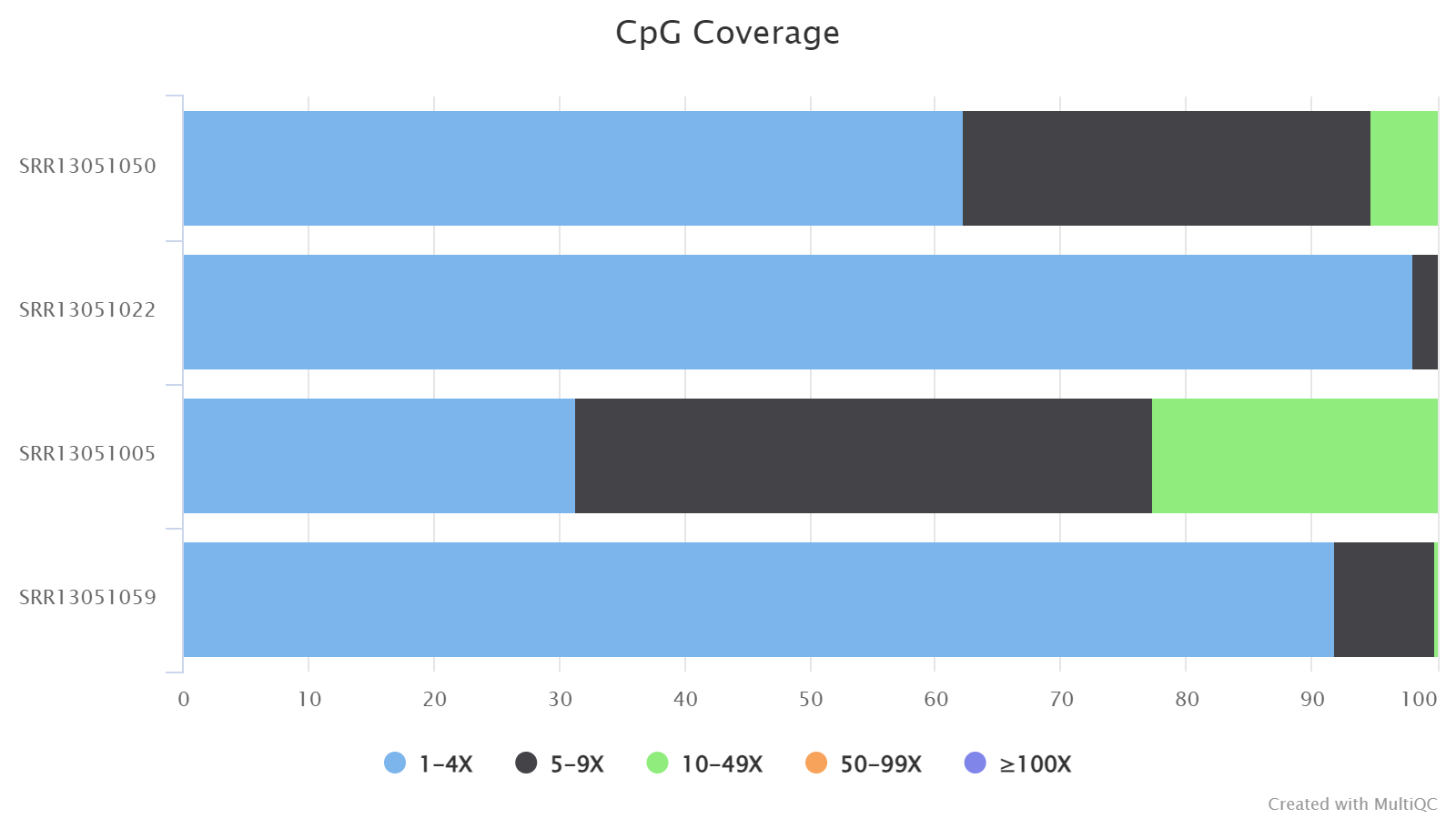
CpG Coverage
This plot presents the number and percentage of cytosines in CpG context under different read coverages. Here, only cytosines covered by at least one read are considered. For easy visualization, the read coverage (aka. read depth) is divided into four ranges: 1-4, 5-9, 10-49, 50-99, >=100.
Software
The software and their corresponding versions used in the pipeline are listed in this section.

Summary
This section shows some parameters used in data analyses, such as trimming parameters, reference genome, etc.
